前言
Spring Bean 的生命周期在整个 Spring 中占有很重要的位置,掌握这些可以加深对 Spring 的理解。
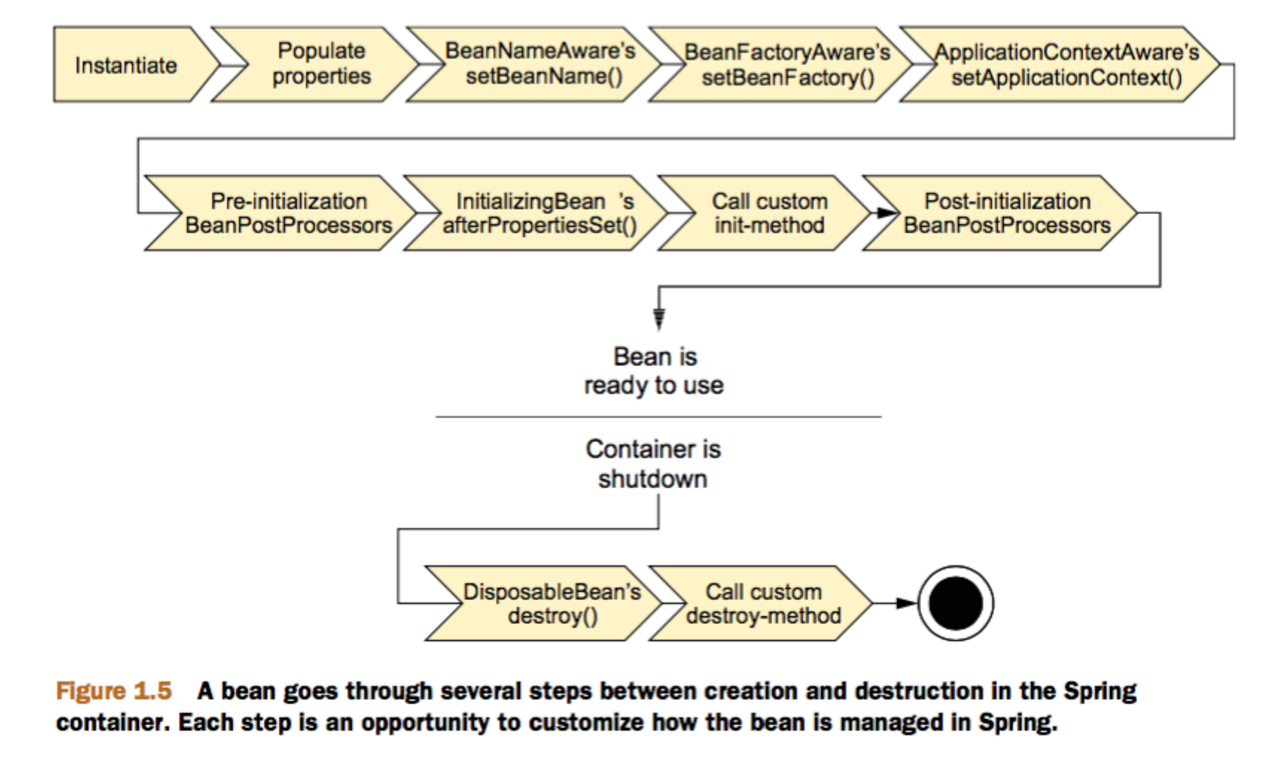
首先看下生命周期图:
再谈生命周期之前有一点需要先明确:
Spring 只帮我们管理单例模式 Bean 的完整生命周期,对于 prototype 的 bean ,Spring 在创建好交给使用者之后则不会再管理后续的生命周期。
[TOC]
注解方式
在 bean 初始化时会经历几个阶段,首先可以使用注解 @PostConstruct, @PreDestroy 来在 bean 的创建和销毁阶段进行调用:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| @Component
public class AnnotationBean {
private final static Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(AnnotationBean.class);
@PostConstruct
public void start(){
LOGGER.info("AnnotationBean start");
}
@PreDestroy
public void destroy(){
LOGGER.info("AnnotationBean destroy");
}
}
|
InitializingBean, DisposableBean 接口
还可以实现 InitializingBean,DisposableBean 这两个接口,也是在初始化以及销毁阶段调用:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| @Service
public class SpringLifeCycleService implements InitializingBean,DisposableBean{
private final static Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(SpringLifeCycleService.class);
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
LOGGER.info("SpringLifeCycleService start");
}
@Override
public void destroy() throws Exception {
LOGGER.info("SpringLifeCycleService destroy");
}
}
|
自定义初始化和销毁方法
也可以自定义方法用于在初始化、销毁阶段调用:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
| @Configuration
public class LifeCycleConfig {
@Bean(initMethod = "start", destroyMethod = "destroy")
public SpringLifeCycle create(){
SpringLifeCycle springLifeCycle = new SpringLifeCycle() ;
return springLifeCycle ;
}
}
public class SpringLifeCycle{
private final static Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(SpringLifeCycle.class);
public void start(){
LOGGER.info("SpringLifeCycle start");
}
public void destroy(){
LOGGER.info("SpringLifeCycle destroy");
}
}
|
以上是在 SpringBoot 中可以这样配置,如果是原始的基于 XML 也是可以使用:
1
2
| <bean class="com.crossoverjie.spring.SpringLifeCycle" init-method="start" destroy-method="destroy">
</bean>
|
来达到同样的效果。
实现 *Aware 接口
*Aware 接口可以用于在初始化 bean 时获得 Spring 中的一些对象,如获取 Spring 上下文等。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| @Component
public class SpringLifeCycleAware implements ApplicationContextAware {
private final static Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(SpringLifeCycleAware.class);
private ApplicationContext applicationContext ;
@Override
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException {
this.applicationContext = applicationContext ;
LOGGER.info("SpringLifeCycleAware start");
}
}
|
这样在 springLifeCycleAware 这个 bean 初始化会就会调用 setApplicationContext 方法,并可以获得 applicationContext 对象。
BeanPostProcessor 增强处理器
实现 BeanPostProcessor 接口,Spring 中所有 bean 在做初始化时都会调用该接口中的两个方法,可以用于对一些特殊的 bean 进行处理:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
| @Component
public class SpringLifeCycleProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor {
private final static Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(SpringLifeCycleProcessor.class);
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
if ("annotationBean".equals(beanName)){
LOGGER.info("SpringLifeCycleProcessor start beanName={}",beanName);
}
return bean;
}
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
if ("annotationBean".equals(beanName)){
LOGGER.info("SpringLifeCycleProcessor end beanName={}",beanName);
}
return bean;
}
}
|
执行之后观察结果:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| 019-03-21 00:40:24.856 [restartedMain] INFO c.c.s.p.SpringLifeCycleProcessor - SpringLifeCycleProcessor start beanName=annotationBean
2019-03-21 00:40:24.860 [restartedMain] INFO c.c.spring.annotation.AnnotationBean - AnnotationBean start
2019-03-21 00:40:24.861 [restartedMain] INFO c.c.s.p.SpringLifeCycleProcessor - SpringLifeCycleProcessor end beanName=annotationBean
2019-03-21 00:40:24.864 [restartedMain] INFO c.c.s.aware.SpringLifeCycleAware - SpringLifeCycleAware start
2019-03-21 00:40:24.867 [restartedMain] INFO c.c.s.service.SpringLifeCycleService - SpringLifeCycleService start
2019-03-21 00:40:24.887 [restartedMain] INFO c.c.spring.SpringLifeCycle - SpringLifeCycle start
2019-03-21 00:40:25.062 [restartedMain] INFO o.s.b.d.a.OptionalLiveReloadServer - LiveReload server is running on port 35729
2019-03-21 00:40:25.122 [restartedMain] INFO o.s.j.e.a.AnnotationMBeanExporter - Registering beans for JMX exposure on startup
2019-03-21 00:40:25.140 [restartedMain] INFO com.crossoverjie.Application - Started Application in 2.309 seconds (JVM running for 3.681)
2019-03-21 00:40:25.143 [restartedMain] INFO com.crossoverjie.Application - start ok!
2019-03-21 00:40:25.153 [Thread-8] INFO o.s.c.a.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext - Closing org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext@3913adad: startup date [Wed Mar 21 00:40:23 CST 2019]; root of context hierarchy
2019-03-21 00:40:25.155 [Thread-8] INFO o.s.j.e.a.AnnotationMBeanExporter - Unregistering JMX-exposed beans on shutdown
2019-03-21 00:40:25.156 [Thread-8] INFO c.c.spring.SpringLifeCycle - SpringLifeCycle destroy
2019-03-21 00:40:25.156 [Thread-8] INFO c.c.s.service.SpringLifeCycleService - SpringLifeCycleService destroy
2019-03-21 00:40:25.156 [Thread-8] INFO c.c.spring.annotation.AnnotationBean - AnnotationBean destroy
|
直到 Spring 上下文销毁时则会调用自定义的销毁方法以及实现了 DisposableBean 的 destroy() 方法。
总结
Spring中Bean的生命周期如下:
Bean容器找到配置文件中Spring Bean的定义。
Bean容器利用Java Reflection API创建一个Bean的实例。
如果涉及到一些属性值 利用set方法设置一些属性值。
如果Bean实现了BeanNameAware接口,调用setBeanName()方法,传入Bean的名字。
如果Bean实现了BeanClassLoaderAware接口,调用setBeanClassLoader()方法,传入ClassLoader对象的实例。
如果Bean实现了BeanFactoryAware接口,调用setBeanClassLoader()方法,传入ClassLoader对象的实例。
与上面的类似,如果实现了其他*Aware接口,就调用相应的方法。
如果有和加载这个Bean的Spring容器相关的BeanPostProcessor对象,执行postProcessBeforeInitialization()方法
如果Bean实现了InitializingBean接口,执行afterPropertiesSet()方法。
如果Bean在配置文件中的定义包含init-method属性,执行指定的方法。
如果有和加载这个Bean的Spring容器相关的BeanPostProcessor对象,执行postProcessAfterInitialization()方法
当要销毁Bean的时候,如果Bean实现了DisposableBean接口,执行destroy()方法。
当要销毁Bean的时候,如果Bean在配置文件中的定义包含destroy-method属性,执行指定的方法。


